How does WDM work?
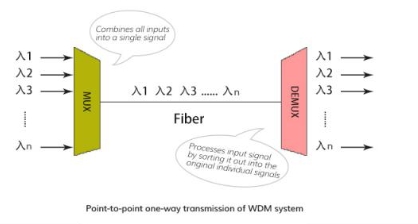
Wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) refers to coupling multiple signals of different wavelengths on a single optical fiber for simultaneous transmission. It usually has multiplexing and demultiplexing. The main function of the multiplexer MUX is to combine multiple signal wavelengths in a single optical fiber for transmission at the transmitting end. The main function of the demultiplexer DEMUX is to separate multiple wavelength signals transmitted in a single optical fiber at the receiving end. The main purpose of wavelength division multiplexing is to increase the available bandwidth of the optical fiber. Therefore, wavelength division multiplexing systems are widely used by telecommunications companies, and can be expanded through WDM without laying more optical fibers.
How to choose: CWDM, DWDM?
CWDM (Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexer) is a sparse wavelength division multiplexer, also known as a coarse wavelength division multiplexer. DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexer) is a dense wavelength division multiplexer.
A big difference between CWDM and DWDM is the different channel spacing between the two. Channel spacing refers to the difference in the nominal carrier frequency of two adjacent channels, which can be used to prevent interference between channels. The wavelength spacing between CWDM channels is 20nm, while the channel spacing of DWDM is 1.6/0.8/0.4 nm (200GHz/100 GHz/50 GHz), which is much smaller than CWDM. The difference in channel spacing also leads to the difference in bandwidth and capacity that CWDM and DWDM can carry. DWDM modules can further increase system bandwidth and capacity by using closely spaced wavelengths to carry more signals on the same optical fiber.
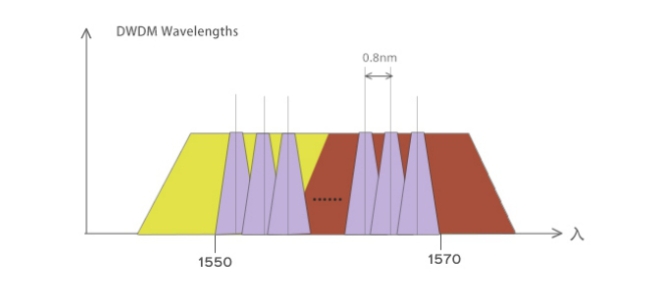
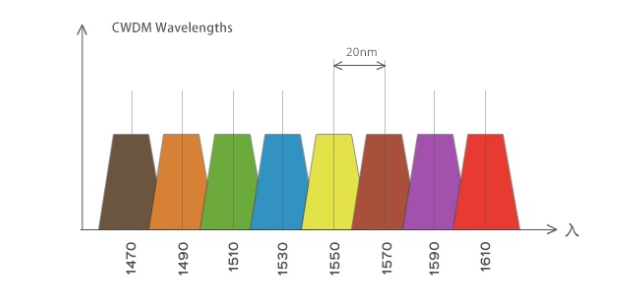
The biggest advantage of CWDM systems is low cost, and the device cost is mainly reflected in filters and lasers. The wide wavelength spacing of 20nm also brings CWDM the advantages of low technical indicators for lasers and simplified structure of optical multiplexers/demultiplexers. The simplified structure and improved yield rate reduce costs. The cost increase of DWDM is mainly due to the high cost of laser diodes and the cooling laser technology used to maintain wavelength stability.
What is CCWDM?
CCWDM is a mini wavelength division multiplexer, a mini version of CWDM. A wavelength division multiplexing technology based on TFF (thin film filter). It works in the same way as CWDM, except that CCWDM uses free space technology, and its package size is greatly reduced compared to CWDM modules, and it has lower insertion loss and better consistency. It can replace CWDM products and be applied in telecommunications, enterprise networks, PON networks, cable TV and other fields.
When choosing CWDM/DWDM/CCWDM solutions, the best solution should be made based on their respective characteristics and differences, and the needs and budget of application scenario construction should be comprehensively considered.