Comparison of several cooling methods of forced air cooling
1. Forced air cooling design principle:
1) Keep the inlet and outlet of the ventilation system as far away as possible to avoid short circuit of air flow.
2) Under the premise of not affecting the electrical performance, the components with large heat generation are grouped together and thermally insulated from other components, which can reduce the air volume and air pressure required by the system, thereby reducing the motor power of the ventilator .
3) Do not reuse cooling air. If used air must be used or used continuously, the order of the air passing through the components should be carefully arranged. The heat-sensitive components and components with low operating temperature must be cooled first to ensure that the coolant has sufficient heat capacity to maintain all parts at a temperature below the operating temperature. Inside.
4) When the cabinet is forced to cool by air, do not let the gap of the cabinet leak air, so as not to affect the heat dissipation effect.
5) The temperature of the cooling air discharged from the enclosure of the electronic device cannot exceed 71°C
6) When calculating the air flow, consider the reduced cross-sectional area due to channel wiring.
7) In order to improve the heat exchange efficiency of the main heating element, the element can be installed in an air duct similar to its shape.
8) The cooling system of the fan of the whole machine reasonably controls and distributes the airflow, and distributes the airflow to each unit and component.
9) The vents must comply with anti-electromagnetic interference, safety requirements, and rain-proof requirements.
10) If a high-speed axial fan is selected, a muffler is required to reduce the noise level.
2. Several cooling methods
1) Direct cooling method as shown in Figure 1
Features:
①Low flow velocity, small heat conduction area and high thermal resistance.
②Generally used below 800W/m²
2) Cold wall cooling method as shown in Figure 2
Features:
①The effect is better than direct cooling method.
②The cold wall is used as a heat exchanger with fins 0.2mm-0.3mm, which is light and has good heat exchange effect.
③The conductive heat resistance between the thermal conductive metal plate and the contact interface is too large, which greatly reduces the cooling efficiency of the cold wall method.
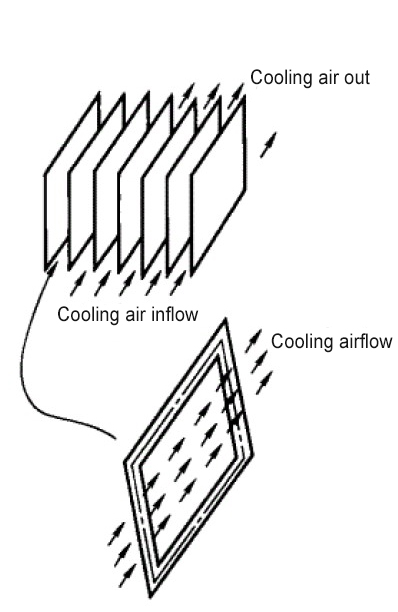
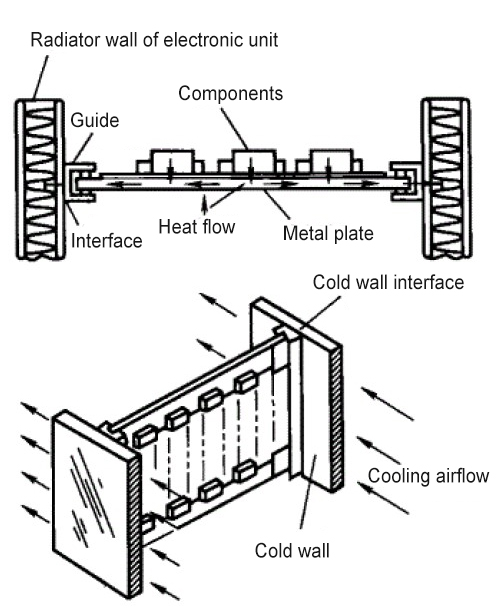
Figure1 Figure2
3) Through-flow cooling method, Figure 3
Features:
①Significantly reduce the problem of excessive heat conduction resistance in the cold wall cooling method.
②Proportional airflow can optimize reliability.
③The most effective one of the three cooling methods.
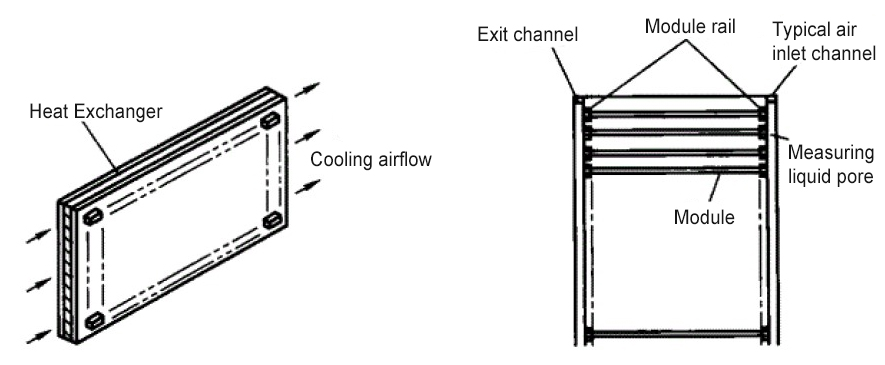
Figure3
3. Comparison of three cooling methods
①Comparison of capacity of three cooling methods for a certain typical circuit template. Table 1, Figure 4
②Comparison of cooling methods. Table 1
| Cooling method | Maximum cooling capacity/(W/㎡) |
| Direct cooling | 800 |
| Cold wall cooling | 1500 |
| Through-flow cooling | 3400 |
Table 1 Comparison of capacity of three cooling methods for a typical circuit board
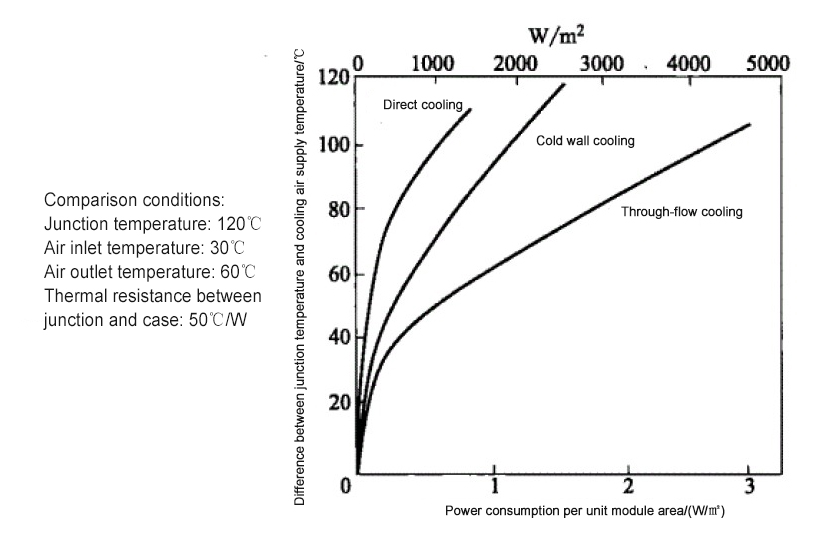
Figure4
| Parameter | Cooling method | ||
| Direct cooling | Cold wall cooling | Through-flow cooling | |
| Cooling effect | low | medium | high |
| Achieve | simple | medium | medium~complex |
| Pressure drop | low | medium | medium~high |
| Component temperature consistency | bad | good | best |
| Air-conditioning utilization | least effective | effective | the most effective |
| Weight | heavy | medium | medium/light |
| Cost | low | medium | medium/high |
Table 2 Comparison of cooling methods